Rationale and Concepts
1. History: Collaborative Work Based on SCM Capabilities
-
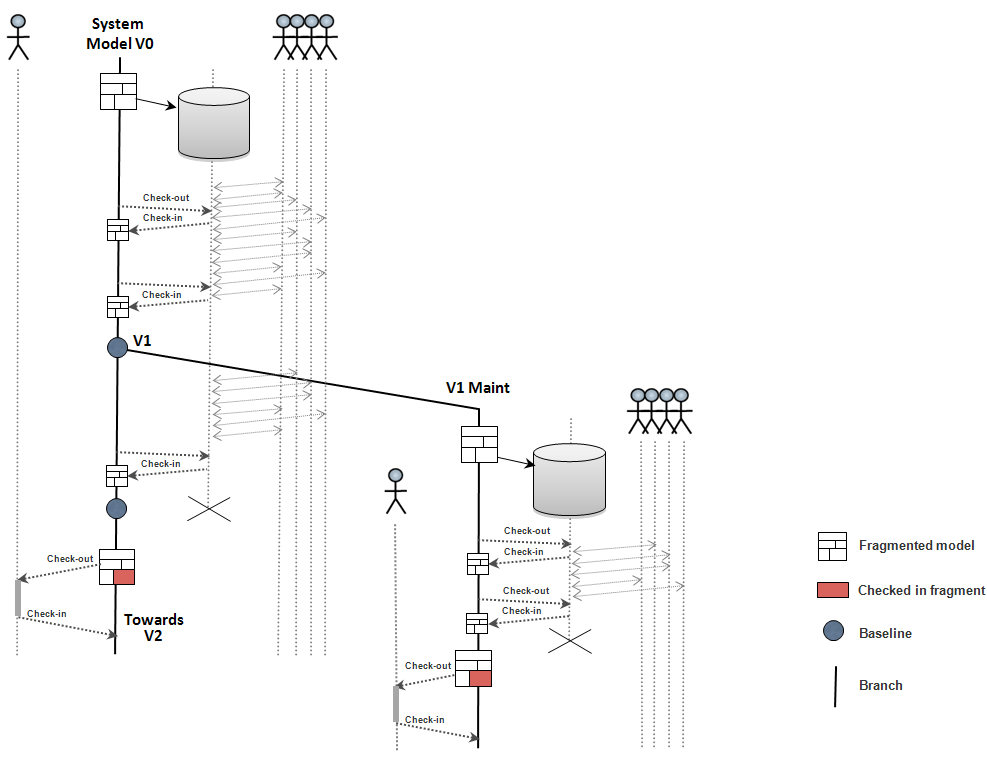
The primary role of a SCM tool is to manage versions of files (models, pieces of code, resources, etc…)
-
A Model is split in files, called fragments
-
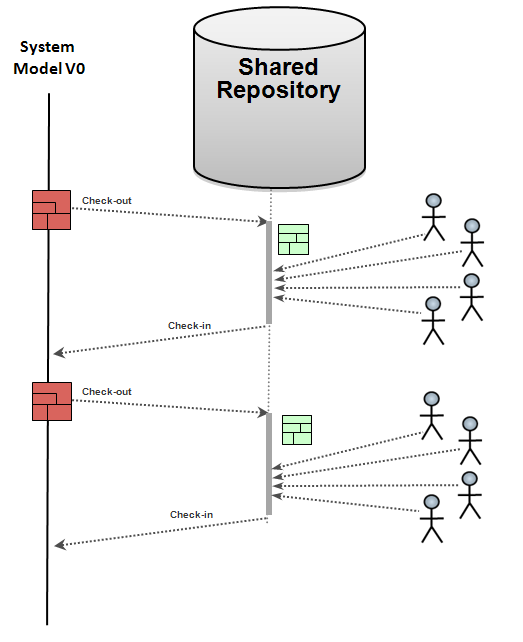
To modify model elements belonging to one specific fragment, users must check out this particular fragment
-
This fragment becomes read-only for the other users (red)
-
A baseline (V1) is put on a regular basis when significant states of the model are reached
-
Branches (V1 Maint) can be created starting from one specific baseline
-
Diff Merge is useful to report changes from one branch to another, but is not used to manage concurrent accesses
-
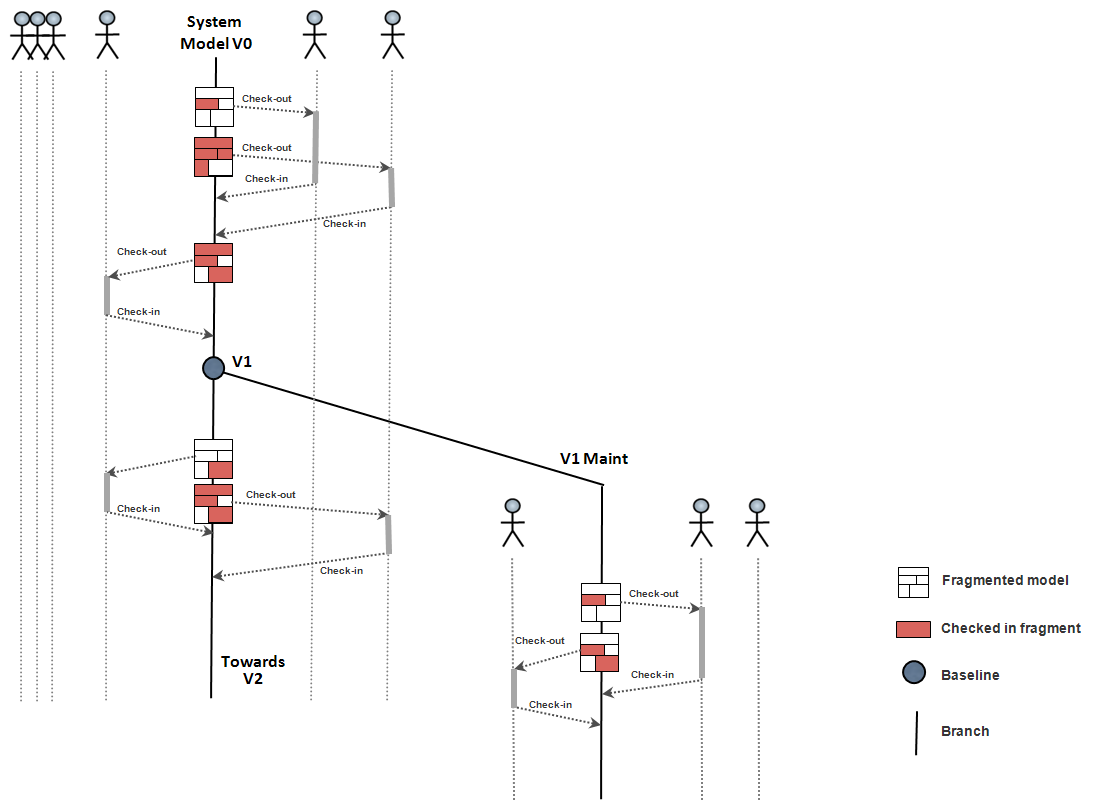
Models are graphs: elements are highly inter-connected (i.e. across fragments)
-
Fragmentation is hierarchical
-
This situation can rapidly lead to strong perturbations:
-
If fragments are too large, users will rapidly be stuck, waiting for particular fragments to be released
-
If fragments are too small, the additional non-functional tasks (check-out, check-in, etc.) becomes too heavy
-
|
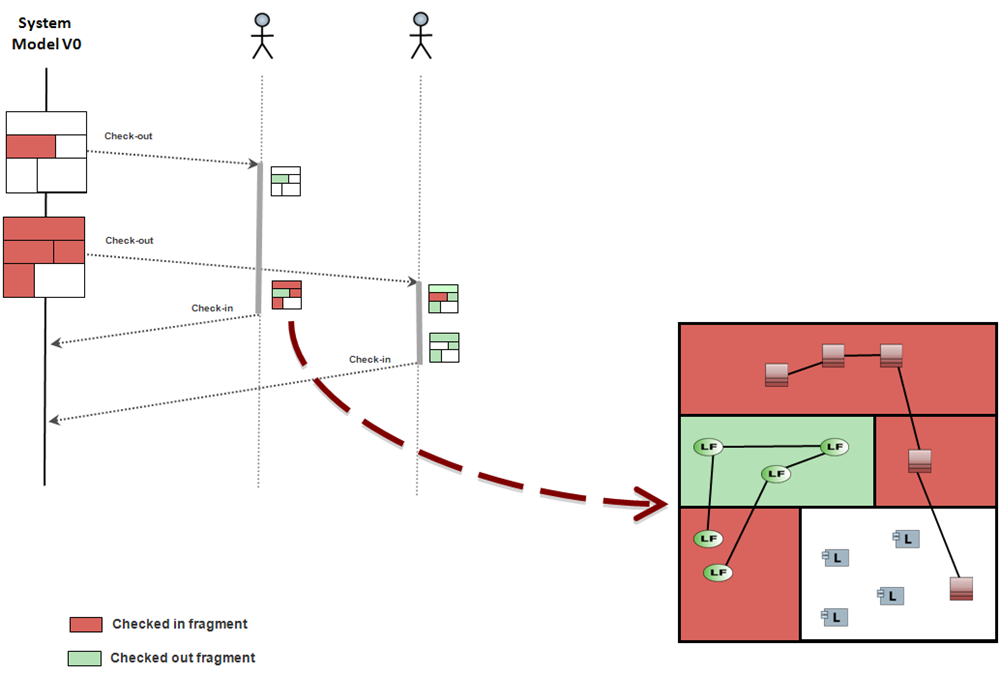
Relying on a SCM tool to manage concurrent accesses is possible, but clearly limited. This main reason is that the needs for managing model versions (genuine objective of a SCM tool) and concurrent accesses are deeply different:
Here, fragments are created to manage concurrent accesses and not anymore because their content has to be versioned. The global idea of Team for Capella Solution is to separate the management of both needs:
|
2. Team for Capella Solution
-
Main Ideas
-
All users shall see an up to date version of the model.
-
Contributors shall be able to work on the same model without interfering, with a granularity as fine as model element.
-
Only one user shall cope with SCM concept.
-
-
Main drivers:
-
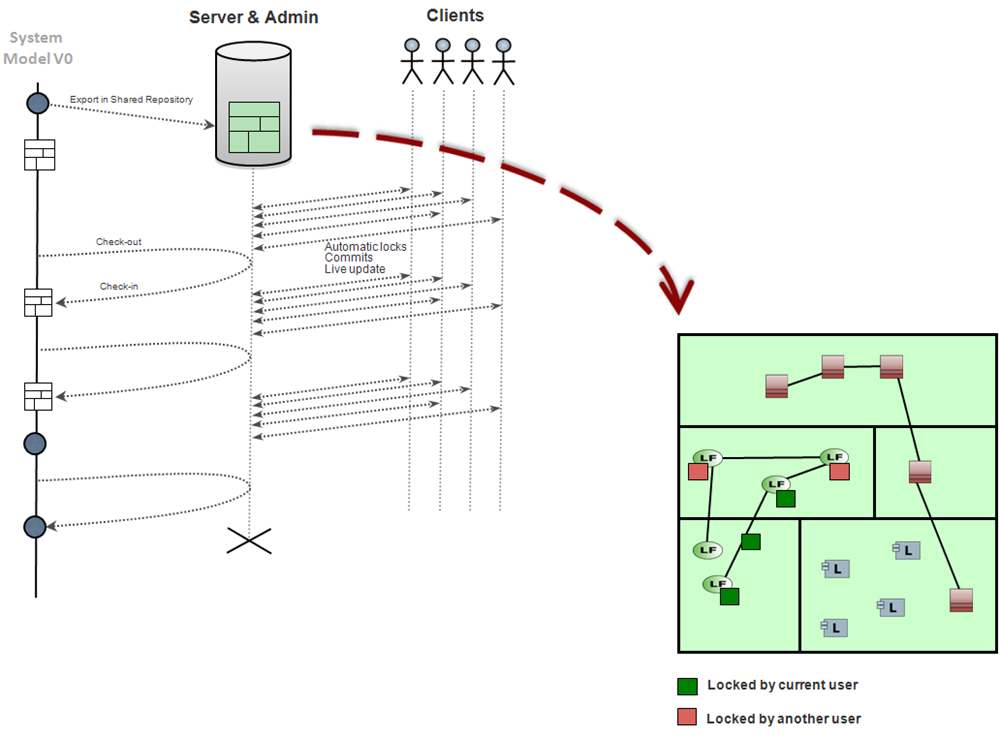
Use a Shared Repository: File-based model is exported in a repository accessible by several users.
-
Manage locks at model element granularity: If one user needs to modify one single element, he should only lock this element.
-
Make locks and update mechanisms automatic: The locking / unlocking / update mechanisms have to be as transparent as possible so that these non-functional activities do not interfere with the engineering activity.
-
|
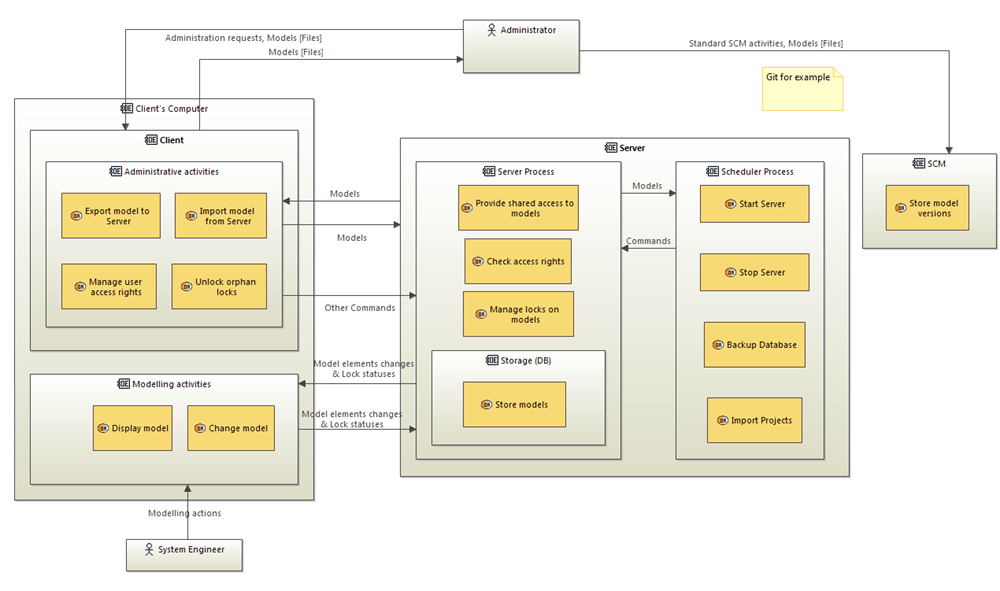
Team for Capella Solution: 3 products.
|
-
Only the Team for Capella Admininistrator has to work with the SCM tool,
-
He/She has to regularly push back shared models to Git,
-
He/She has to created Baselines when necessary,
-
-
The Team for Capella Server is responsible for managing fine-grained concurrent accesses to the model,
-
Users connect to the shared repository through Team for Capella Client,
-
Team for Capella Client is connected in live mode: it always shows the latest state of the model shared in the repository,
-
-
Fragmentation is only used for model versioning purpose.
3. Shared Repositories and Configuration Management
-
Shared repositories are not permanent
-
They live as long as concurrent accesses are necessary on one version of a model
-
-
It is still possible for users to contribute directly through Git once the repository has been shut down
-
Diff Merge is useful to report changes from one branch to another, but is not used to manage concurrent accesses